Managing Kubernetes configurations can be complex, especially with the plethora of tools available for configuring workloads and deploying applications. Kustomize stands out as a unique and popular tool for generating, transforming, and patching Kubernetes configurations without introducing custom DSLs or parameter-driven templates.
In this post, we will explore:
- Why Kustomize was created
- Its core principles and key features
- Comparisons with other tools like Helm
- Where it excels and the challenges you might face
- How to get started with a sample application and code
By the end, you’ll see how Kustomize’s transformation-based approach can simplify configuration management in your Kubernetes workflows.
Why Kustomize Was Created
From the early days of Kubernetes, the ecosystem produced numerous tools for configuring workloads, yet no single tool emerged as the definitive solution. In 2016, Google Cloud partnered with Deis (later Microsoft) to develop Helm v2, which became a central tool for packaging and deploying Kubernetes applications. However, the Kubernetes core project needed its own minimal configuration solution to handle specific use cases, including:
- Add-on management
- Declarative specification of
kubectlcommands - Patching configurations for rolling updates and environment-specific customizations
Kustomize was born (initially called kinflate) to address these needs. Its primary goal was to be Kubernetes-native and avoid custom DSLs or parameter-driven templates, providing a declarative, composable configuration management approach.
The Core Principles of Kustomize
Kustomize’s philosophy revolves around the idea that Kubernetes configuration should:
- Use Kubernetes API resource specifications as the declarative data model.
- Avoid parameter-driven generators or custom DSLs.
- Remain extensible and composable for a wide range of use cases.
By adhering to Kubernetes’ native structure, configurations remain simple, standardized, and easy to manipulate.

Key Features of Kustomize
1. Patching and Overlays
A central feature of Kustomize is its patching mechanism using strategic merge patches. You can modify configurations declaratively by creating overlays that specify variations of a base configuration for different environments (development, staging, production, etc.).
Below is a simplified example of how to define base resources in kustomization.yaml:
# Base kustomization.yaml
resources:
- deployment.yaml
- service.yaml
Then, in your overlay, you can patch the base configuration to customize it for a specific environment:
# Overlay kustomization.yaml
resources:
- ../base
patches:
- deployment-patch.yaml
Where deployment-patch.yaml might look like:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
replicas: 3 # Overriding the replicas for this environment
With this structure, you manage environment-specific configurations without duplicating entire files.
2. Resource-Aware Transformations
Kustomize supports resource-aware transformations that leverage the Kubernetes schema:
- Setting labels and annotations
- Updating container images
- Adjusting replica counts
- Modifying resource requests and limits
Kustomize also offers a plugin framework, allowing you to extend its functionality for custom transformations.
3. Composability
Instead of generating configurations from scratch (like some templating tools), Kustomize composes and transforms existing resources. This approach makes it easy to integrate with other tools such as Helm—allowing you to leverage Helm charts while still applying Kustomize overlays.
Comparing Kustomize to Other Tools
Kustomize vs. Helm
Helm is a powerful tool for packaging and deploying Kubernetes applications. It uses parameter-driven templates for customization, which can be both powerful and complex. Kustomize, by contrast, transforms existing Kubernetes YAML files in a declarative manner and avoids custom DSLs.
- Helm excels when you need a robust packaging solution (e.g., for distributing applications).
- Kustomize excels when you want a minimalistic, Kubernetes-native tool that can patch and overlay configurations without introducing additional templating layers.
Kustomize vs. General JSON/YAML Tools
General-purpose JSON/YAML editors (like yq) can manipulate YAML files but lack Kubernetes-specific context. Kustomize, however, uses Kubernetes’ schema information to perform context-aware transformations, making it more specialized and effective for Kubernetes configuration management.
Where Kustomize Excels
- Declarative Approach: Sticking to Kubernetes’ declarative nature simplifies configuration.
- Environment Customization: Overlays let you manage multiple environments cleanly.
- Extensibility: The plugin framework supports custom transformations.
- Composability: Works well with other tools (e.g., Helm) thanks to its transformation-based approach.
Challenges with Kustomize
While Kustomize is powerful, it’s not without its drawbacks.
- Learning Curve: Overlays and transformations can initially feel confusing.
- Limited Packaging: Unlike Helm, it doesn’t provide packaging or release management features.
- Complex Scenarios: Deeply nested configurations can become cumbersome compared to parameterized templates.
Sample YAML Demonstrating a Common Challenge
# Suppose you have multiple patches for a single Deployment
# This can become tricky to maintain if you have many environment-specific changes.
patches:
- deployment-replicas-patch.yaml
- deployment-image-patch.yaml
- deployment-resources-patch.yaml
- deployment-labels-patch.yaml
# Over time, these patches can grow in number and complexity,
# making your overlay structure more difficult to navigate.
Maintaining numerous patches for complex applications can be a bit unwieldy, especially when you need to combine them with other tooling.
How to Get Started
- Kustomize Installation
- You can install it as a standalone binary or use the version bundled with
kubectl(e.g.,kubectl kustomize).
- You can install it as a standalone binary or use the version bundled with
- Organize Your YAML Files
- Create a base directory containing original manifests (
deployment.yaml,service.yaml, etc.). - Create environment-specific overlay directories (e.g.,
overlays/dev,overlays/staging, etc.) with their ownkustomization.yamlfiles.
- Create a base directory containing original manifests (
- Apply Your Config
- Render your manifests using
kustomize build <path>orkubectl apply -k <path>.
- Render your manifests using
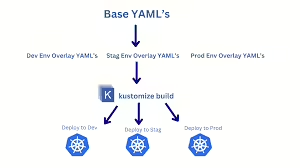
Sample App and Code
Below is a very simple setup to illustrate how you can structure a Kustomize-based project. Let’s assume you have a minimal Node.js application running in Kubernetes.
.
├── base
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── service.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── deployment-patch.yaml
└── prod
├── kustomization.yaml
└── deployment-patch.yaml
base/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sample-node-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sample-node-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sample-node-app
spec:
containers:
- name: node-container
image: node:16
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
base/service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sample-node-app-svc
spec:
selector:
app: sample-node-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 3000
protocol: TCP
base/kustomization.yaml
resources:
- deployment.yaml
- service.yaml
overlays/dev/kustomization.yaml
resources:
- ../../base
patches:
- deployment-patch.yaml
overlays/dev/deployment-patch.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sample-node-app
spec:
replicas: 2
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: node-container
image: node:16-alpine
Use the following command to apply the dev overlay:
kubectl apply -k overlays/dev
This example illustrates how to manage multiple environments without duplicating entire manifests.
Final Thoughts
Kustomize’s transformation-based approach bridges the gap between simplicity and flexibility. Whether you use it standalone or alongside other tools like Helm, Kustomize provides a declarative and composable way to manage Kubernetes configurations at scale.
Do you already use Kustomize in your Kubernetes workflows? How does it compare to other tools you’ve tried? Let us know in the comments below or connect with us at Collabnix.
Thanks for reading! If you found this article helpful, be sure to check out our other Kubernetes-related posts on Collabnix. Feel free to share this article and leave your thoughts in the comment section below.
